TABLE OF CONTENTS
An invoice is a transactional document that sellers provide to buyers for payment of goods or services. This transaction can take place before, during, or after the exchange of said goods and services.
A typical invoice is a structured document that includes the details of the buyer and seller, the goods or services, the dollar amount, tax, and payment terms. Invoices are considered legally binding depending on the type of invoice used for a transaction.
Is an invoice a bill or a receipt?
Invoices should not be confused with bills or receipts. While invoices and bills share similarities, invoices are structured documents explicitly designed to ask for payment for any of goods and services provided. A bill is a more informal document telling the customer what they owe.
The difference between an invoice and a receipt is that a receipt is a proof of payment document. A receipt is provided to the buyer of goods and services for their own use as proof of purchase.
Types of invoices
It’s important to use the right invoice type for your business. Let’s look at a couple of different examples and what they mean in the context of the payment process.
Sales invoice
A sales invoice is a common type of invoice you send to a client, customer, or buyer, from whom they pay. It is one of the most common invoices and is exchanged by small businesses all across Australia.
Tax invoices
Tax invoices include the goods and services tax on top of the dollar cost of the goods and services provided. If you are registered for GST, you must provide tax invoices. These are considered a legally binding agreement between the buyer and seller.
Pro forma invoice
A pro forma invoice is a non-binding document sent before the buyer and the seller confirm prices. Pro forma invoices are generally used for the following circumstances before a final invoice is sent:
- To begin the cost confirmation process between the parties
- A starting point for the negotiation of costs between parties to find an agreed-upon price
- Part of an import/export manifest between parties when goods go through customs.
Commercial invoice
A commercial invoice is a foreign trade document that accompanies a customs manifest. If you send goods overseas, you would use a commercial invoice as part of the payment and shipping process.
Electronic invoices
Electronic invoices are where businesses send invoices electronically between each other via their accounting software. Businesses use electronic invoices more frequently because sending them this way is more cost-effective and efficient, helps facilitate online payment, and reduces manual handling and paper use. Typically, electronic invoices are sent via accounting and invoice software to another business’s software.
What is in an invoice?
What information is required on an invoice? An invoice should include the following information:
Invoice details
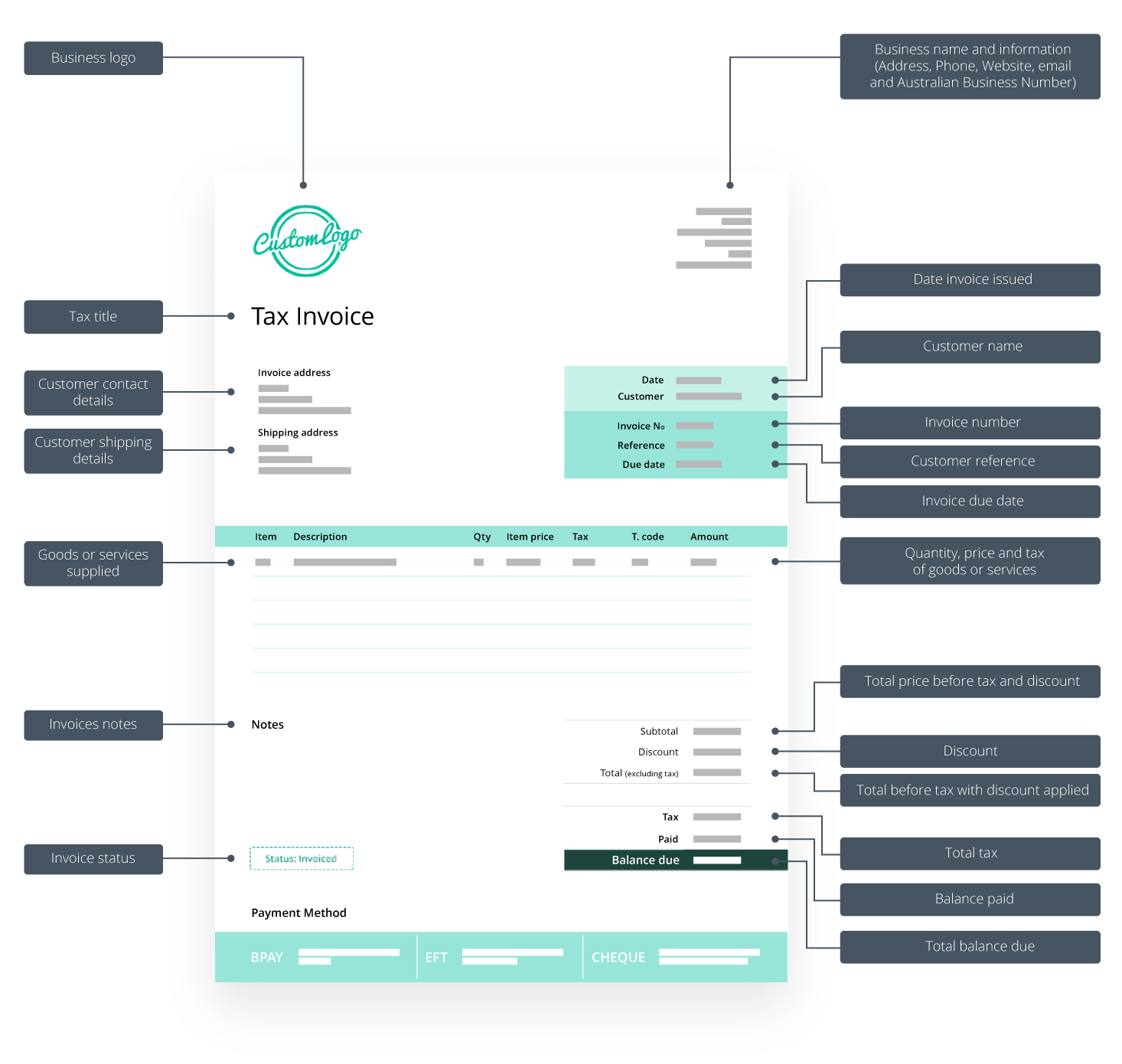
- Logo: Your custom business logo.
- Tax title: Your invoice requires a title. If you’re registered for GST, the title should be ‘Tax Invoice’. If you’re not registered, you can name the document ‘Invoice’.
- Date invoice issued: The date the invoice is issued.
- Customer name: The customer’s name.
- Invoice number: A unique invoice number distinguishes your invoices from each other. This is important for payment tracking and record-keeping.
- Customer reference: If your customer has provided you with a purchase order number, you must include this on the invoice. If you haven’t been given this information, you can list the name of your contact person at the business.
- Invoice due date: The number of days (from the invoice date) the buyer must pay the seller, and the payment due date.
Your business details
- Business name and information of seller: Your business name, address and contact details. Freelancers and sole traders can use a personal name. Include the details of the person to contact if the customer has queries about the invoice.
- Tax or business number: Your Australian Business Number (ABN). If you don’t add one, the customer or business must withhold 47% of the amount and send that to the Australian Tax Office.
Customer details
- Customer contact information/buyer identity: The customer’s name and address to which to send the invoice. If it’s an organisation, check their legal name as it could differ from the trading name you’re familiar with.
- Customer shipping address: The name and address where the goods will be sent. This may be optional if it’s the same as the invoicing address.
List of goods or services supplied
- Item description: A brief description of each product or service you supplied.
- Quantity: The number of items you supplied or the number of hours you’re charging for.
- Item price: The price per unit, hour, or the fixed price you agreed on upfront.
- Tax component: The amount of tax that applies.
- Amount: The price for that item or service.
Amount owed
- Subtotal: The total before GST of all the goods and services listed. Make sure you apply any discounts you’ve offered and include any shipping charges.
- Discount: Any discount that may apply.
- Total (excluding tax): Total amount before tax with discount applied.
- Tax: Total tax.
- Paid: Balance paid.
- Balance due: Total balance owing.
Payment terms
- Discount or late payments: The amount of any on-time discounts or late fees.
- Additional statement: If more information is needed regarding payment reminders and recurring invoices.
- How the buyer can pay the invoice: List the methods of payment you offer, e.g., internet banking, credit card, BPAY, PayPal, cash, or cheque. Include your bank account number or a link so customers can pay online.
Why is invoicing important?
Invoicing is important because it is how most businesses receive payment. Invoices affect the flow of revenue into your business. Without invoices, you cannot track payments, keep tax compliant and keep your cash flow ongoing.
Because the invoicing process is part of how a business receives income, it is essential that you have the right accounting and invoicing software so that you can get paid faster and remain tax compliant.